A working Houston Independent School District (ISD) graduate who has an associate degree or higher makes an annual salary of $24,400 more, on average, than a graduate with no postsecondary education. Historically, districts have focused on ensuring students graduate from high school, but school districts also have a responsibility to prepare students for postsecondary success.
A New College- and Career-Readiness Goal
A key responsibility of the school board is to set the district’s vision and ensure the system remains accountable for achieving that vision. In November 2023, the Houston ISD Board of Managers set and adopted ambitious five-year goals focused on improving student outcomes. During the goal-setting process, EdTrust and the Citywide Coalition on Education advocated for the adoption of a goal that measures college and career readiness.
Subsequently, the Board of Managers adopted a goal (Goal 3) that does just that: The goal is for the percentage of students graduating Texas Success Initiative (TSI)-ready and with an industry-based certification (IBC) to increase from 11% for 2021–2022 graduates to 26% for 2026-2027 graduates.
Why This Goal Matters
Preparing students for life after high school, whether they choose to attend college or go directly into the workforce, is one of the core purposes of education. By emphasizing both college and career readiness, HISD aims to equip students with the skills and qualifications needed to succeed in higher education and/or secure well-paying jobs.
This goal will ensure that students not only graduate but also do so with meaningful credentials in hand — such as certifications in high-wage and high-demand fields — or advanced courses under their belt that demonstrate that they are ready for credit-bearing coursework in college. This increases their chances of achieving a living wage, opens more career opportunities, and improves their potential for long-term success. It also gives students the power to choose their own path, giving them the autonomy to continue their education or start a career immediately after high school.
Measuring College and Career Readiness
To accurately assess students’ likelihood of future postsecondary success, the district must look beyond traditional measures of academic success like GPA. Fortunately, the criteria for measuring college and career readiness generally include, but are not limited to, completing dual-credit courses, taking coherent career and technical (CTE) coursework, earning an associate degree. Goal 3 also includes TSI criteria, such as achieving a passing score on exams like the SAT, ACT, or the Texas Success Initiative Assessment (TSIA), thereby demonstrating a student’s ability to handle college-level coursework.
Another important measure that is predictive of future long-term success is earning an industry-based certification. Research shows that students who earn a certification are more likely to matriculate in higher education. And having an industry-based certification (IBC) shows that a student has mastered a specific set of skills or knowledge that’s relevant to a particular job within an industry. Examples include programming, web design, and welding.
Goal 3 measures both college and career readiness and monitors the progress of students who are both meeting the TSI criteria and earning an industry-based certification. This goal holds the school system accountable for putting students on a path to earn a living wage and to succeed in higher education after high school graduation.
Current Outcomes for HISD Students
When the board adopted Goal 3 a year ago, 11% of graduates (of the Class of 2022) met the criteria of a passing TSI score and earning an IBC. This month, the HISD Board of Managers monitored progress on this goal. Note that the data in the progress-monitoring report is for the Class of 2023, since there is a one-year lag in reporting on college- and career-readiness outcomes.
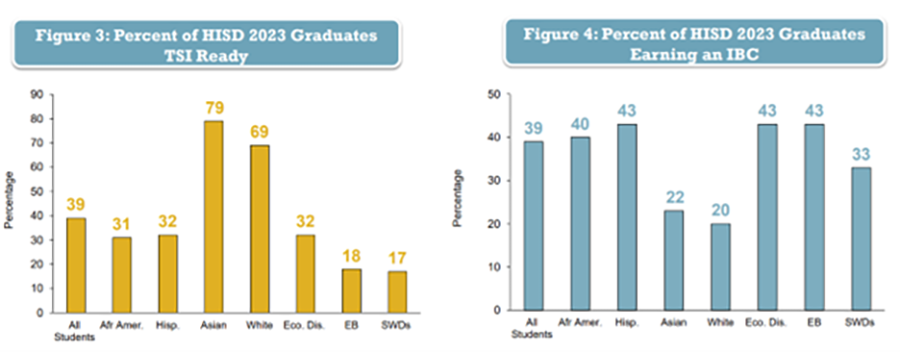
About 12% of graduates from the Class of 2023 hit the Goal 3 target of both TSI readiness and earning an IBC. All student groups met the annual target — except for white and Asian students, who historically in HISD earn IBCs at lower rates, but disproportionately meet TSI criteria at much higher rates (79% and 69% respectively for the Class of 2023).
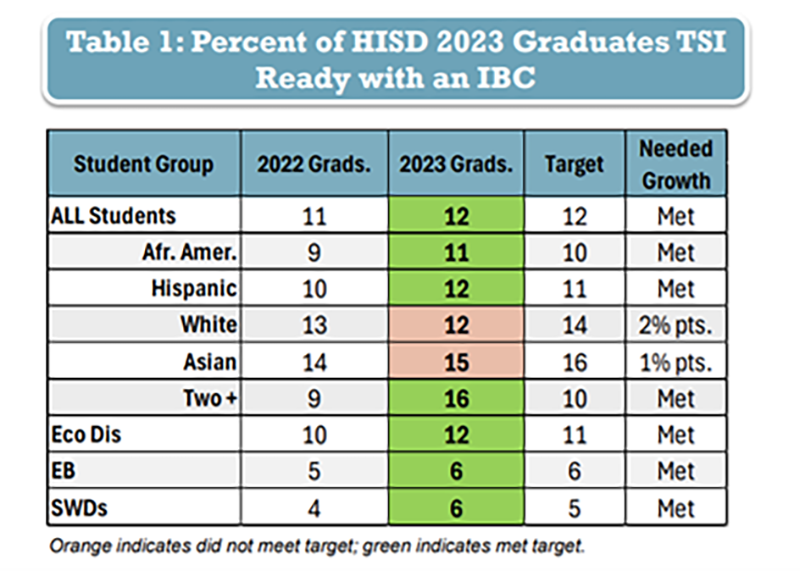
Source: Agenda Item #2 – Presentation of Goals 3 and 4: September Goal Progress Report